How much protein per day is needed?
Want to know how much protein per day you need? What the average is and how that varies when you exercise? As well as which foods you can take more of, to meet your protein needs per day? In this article you will find the answer to all your questions and more. Find out how many grams of protein per day you need, what protein-rich foods are, and why it’s so important to eat enough protein – but not too much.
How much protein per day needed on average?
A person’s average protein requirement per day depends on body weight. For every kilogram of body weight, you need 0.83 grams of protein daily. Do you weigh 75 pounds? Then you should eat about 62.26 grams of protein. You can get there pretty easily with a healthy and varied diet. In fact, protein is found in all kinds of foods. We’ll come back to this later, so you can focus on protein-rich foods if you want to.
How many grams of protein per day for an athlete?
If you do strength training or endurance sports, then the answer to the question “how much protein per day” is different than for an average person. This is because the need for protein is greater when you exercise. After intensive exercise, you need extra protein for good muscle recovery. Especially when you want to grow more muscles, it is important to combine training with protein-rich food. Depending on your goals, keep about 1.2 to 2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight as a guideline.
Is it necessary to consume extra high-protein foods?
In most cases, it is not necessary to consume additional high-protein foods to meet your protein needs per day. With an average diet, you already get about 95 grams of protein as a man and about 70 grams as a woman. This is more than enough. Would you still like to take in more protein? Then you can achieve that by adding certain foods particularly rich in protein to your diet. But beware: if you eat more protein than you need, it will be stored as fat or used as energy. That’s something you want to avoid.
What are examples of high-protein foods?
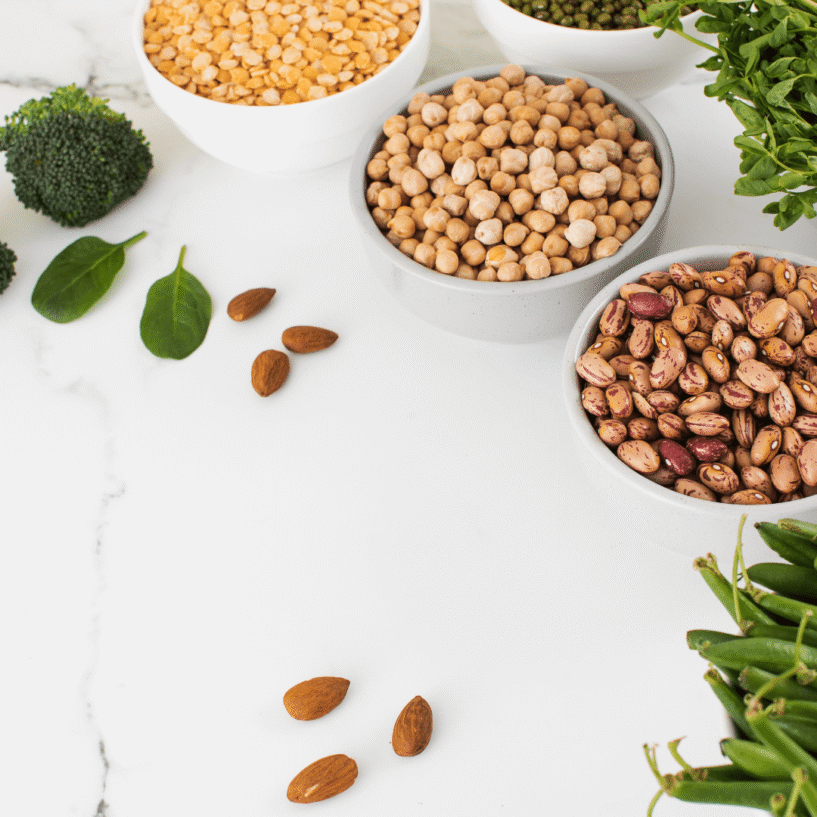
Examples of protein-rich foods include meat, fish, poultry, eggs, cheese and other dairy products. But there are also numerous plant-based sources of protein. These include yogurt or soy products such as tofu and tempeh. Or legumes such as beans, lentils and chickpeas. Grains, nuts and seeds are also high in protein. As you can see, it’s easy to eat enough protein as both a carnivore and vegetarian.
Vegetables high in protein
Besides legumes, there are a lot of other types of vegetables that are high in protein. Take beans, for example. There is as much protein in 100 grams of beans as in one egg. That’s about 6 grams. Asparagus – at one gram each – also contains an awful lot of protein. As do kale (4.3 grams of protein per 100 grams), Brussels sprouts (3.8 grams) and broccoli (3.3). But mushrooms (2.7 grams), spinach (2.5 grams) and cauliflower (2 grams) are also relatively rich in protein.
Why is it important to eat enough protein?
Proteins are important nutrients. They are macronutrients that provide our bodies with energy. Proteins help build and repair our muscles. But they also protect and improve a host of other types of tissue in our bodies. Furthermore, protein is good for digestion, metabolism and brain function, among other things. So plenty of reasons to want to meet your daily protein needs.